Blockchain technology has gained immense popularity due to its decentralized, transparent, and tamper-resistant nature. It underpins cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum and is being adopted in various industries, from finance to supply chain management. However, a critical question remains: How secure is blockchain? In this article, we will explore blockchain’s security model, its strengths, vulnerabilities, and best practices to ensure its safety.
The Fundamentals of Blockchain Security
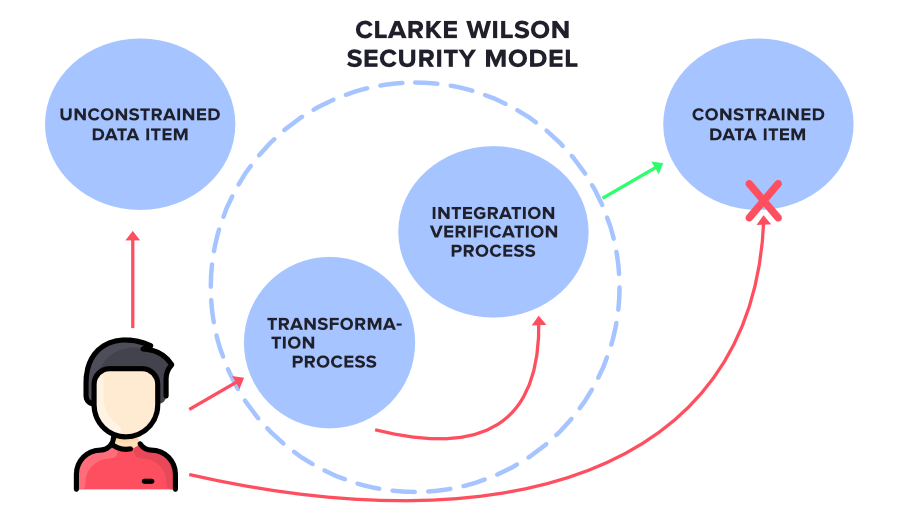
Blockchain security is built on three core principles:
- Decentralization – Unlike traditional centralized databases, blockchain operates on a distributed network of nodes, making it less susceptible to single points of failure and attacks.
- Cryptographic Security – Each transaction is encrypted using advanced cryptographic algorithms, ensuring data integrity and protection from unauthorized access.
- Consensus Mechanisms – Blockchains use mechanisms like Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions, preventing fraudulent activities such as double-spending.
Key Security Features of Blockchain
1. Immutability
Once a block is added to the blockchain, altering it becomes nearly impossible due to cryptographic hashing and the linking of blocks. This prevents fraud and unauthorized modifications.
2. Transparency and Trust
Blockchain transactions are recorded on a public ledger, which can be verified by all participants. This transparency enhances trust and accountability in digital transactions.
3. Cryptographic Hashing
Every block contains a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block, making it highly resistant to tampering. Even a small change in transaction data will generate a completely different hash, alerting the network to a potential breach.
4. Smart Contracts Security
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with predefined rules. They eliminate intermediaries but must be carefully coded to avoid vulnerabilities like reentrancy attacks and logic flaws.
Potential Vulnerabilities in Blockchain Security
Despite its robust security model, blockchain is not immune to threats. Some key vulnerabilities include:
1. 51% Attacks
If a single entity gains control of more than 50% of the network’s mining power, it can manipulate transactions, enabling double-spending or blocking transactions.
2. Private Key Theft
Blockchain relies on public-private key cryptography. If a user’s private key is stolen, attackers can gain full control over their digital assets.
3. Smart Contract Bugs
Poorly written smart contracts can be exploited by hackers, leading to financial losses. This has happened in notable cases like the DAO hack on Ethereum.
4. Sybil Attacks
In this attack, a single adversary creates multiple fake nodes to gain disproportionate influence over the network, potentially manipulating transactions or consensus.
Enhancing Blockchain Security
To mitigate risks, various security measures should be implemented:
- Use Strong Cryptographic Algorithms – Employing advanced encryption standards ensures data security and prevents unauthorized access.
- Regular Audits – Smart contracts and blockchain applications should undergo rigorous security audits to detect vulnerabilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) – Adding extra layers of authentication reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Cold Wallets for Storage – Storing private keys in offline cold wallets minimizes exposure to online attacks.
- Adopting Advanced Consensus Mechanisms – New mechanisms like Proof of Authority (PoA) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS) offer enhanced security compared to traditional PoW models.
Also Read: NFTs and Blockchain: The Digital Ownership Revolution
Conclusion
Blockchain is one of the most secure technologies available today, but it is not infallible. While its decentralization, cryptographic security, and consensus mechanisms provide strong protection, vulnerabilities such as 51% attacks, private key theft, and smart contract bugs highlight the need for ongoing improvements. By implementing best practices and staying vigilant, businesses and individuals can harness blockchain’s power while mitigating potential risks.